Within SAP Extended Warehouse Management (EWM), master data is systematically categorized into two main types, each playing a crucial role in maintaining accurate and current information. The first category encompasses external data, requiring replication from SAP ERP or SAP S/4HANA into the SAP EWM environment. This external dataset includes pivotal information such as material master, vendor master, customer master, and plant details. The replication process is essential to uphold data accuracy within the SAP EWM system. Conversely, the second category pertains to internal data, generated exclusively within the SAP EWM environment. This internal data consists of storage bin master data and packaging specification master data, typically established during the initial setup of the SAP EWM system and subsequently maintained within the system.
Emphasizing the significance of the master data replication process, especially from SAP ERP or SAP S/4HANA to SAP EWM, is vital for the seamless operation of the overall system setup. This process ensures the consistency of data between the SAP EWM system and the source systems (ERP or S/4HANA). Furthermore, it guarantees that any alterations made to the data in the source systems are accurately reflected in the SAP EWM system. As we delve into the intricacies of data transfer processes, it’s crucial to differentiate between SAP NetWeaver deployments, embedded EWM deployments, and decentralized EWM deployments. Each deployment scenario involves unique considerations and methodologies to optimize the data transfer between systems, ensuring a harmonized and efficient overall operation.
SAP NetWeaver Data Transfer Strategies
In the illustration provided, facilitating the implementation of SAP EWM versions 9.5 and below via SAP NetWeaver SAP Business Suite involves the utilization of CIF technology. This system employs CIF as a primary mechanism for transferring master data between SAP ERP and SAP EWM. CIF is specifically designed for the seamless exchange of data between SAP ERP and SAP Supply Chain Management (SAP SCM).
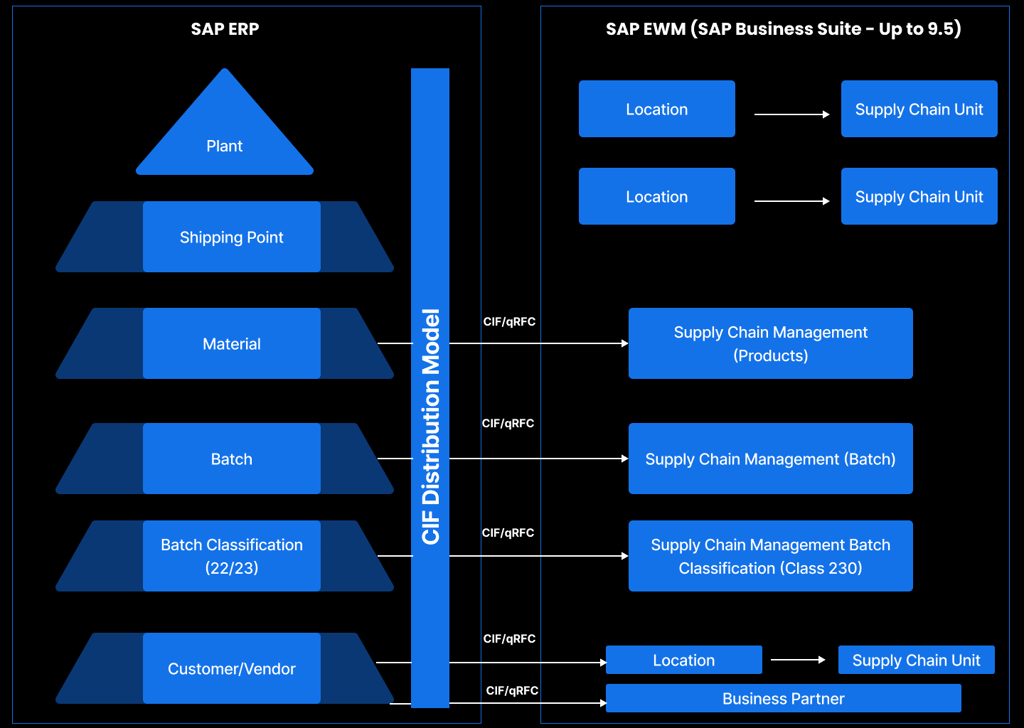
In the context of SAP EWM, the data transfer process involves a unidirectional flow where only master data is moved from SAP ERP to SAP EWM utilizing CIF. Conversely, for transactional data, including inbound and outbound delivery documents originating from SAP ERP, integration into SAP EWM relies on the queued remote functional call (qRFC) technology. This approach establishes asynchronous communication between the two systems, offering a dependable and efficient means of transferring transactional data from SAP ERP to SAP EWM.
Efficient Data Transfer Strategies in Embedded EWM Deployments
As depicted, within an embedded EWM system, the transfer of master data through CIF is unnecessary. It’s important to highlight that despite this, the transmission of transaction data from SAP S/4HANA to embedded EWM still necessitates the utilization of queued remote functional call (qRFC) technology.
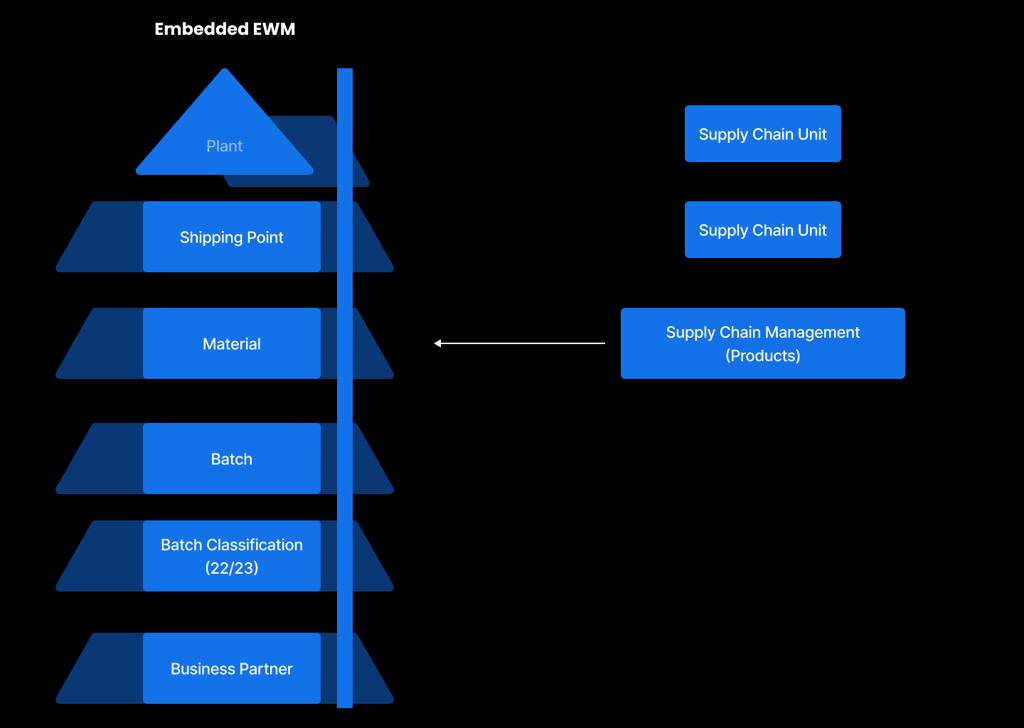

qRFC, a communication method employed by SAP systems, serves as a reliable and efficient means of transferring data between systems. This approach allows for the batched transmission of data, mitigating the risk of errors or data loss. In the context of embedded EWM, transaction data encompasses crucial information related to goods movements, inventory updates, and warehouse operations. The utilization of qRFC facilitates the timely and accurate transmission of transaction data from SAP S/4HANA to embedded EWM. This capability ensures seamless integration between the two systems, providing real-time visibility into warehouse operations and inventory levels.
It’s important to note that, in embedded EWM, the transfer of master data via CIF is unnecessary. However, CIF-based data transfers may still be required for other SAP components or systems. Therefore, a crucial step involves evaluating the specific requirements of each scenario to determine the appropriate data transfer method. This strategic assessment ensures optimal data flow and integration across different SAP elements.
Strategies for Decentralized EWM Data Transfer
As illustrated in the following diagram, in a decentralized EWM implementation with SAP S/4HANA, the application link enabling (ALE)/IDoc technique is utilized for transferring material master data from SAP ERP to SAP EWM. Furthermore, the data replication framework (DRF) technique is employed for the transfer of customer and vendor master data, commonly known as business partners in decentralized EWM. On the other hand, the CIF technique continues to be employed for the transfer of specific master data, such as packaging specifications, from SAP ERP to SAP EWM.
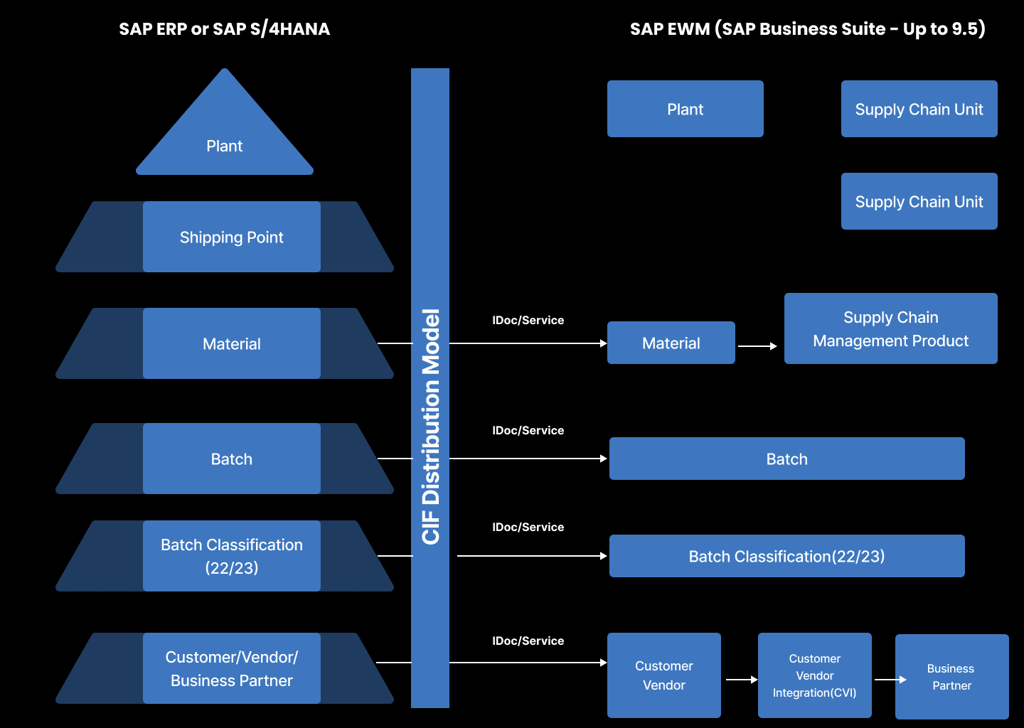

Furthermore, specific transactional data types, including inbound and outbound delivery documents originating from SAP ERP, are seamlessly integrated into SAP EWM using qRFC technology. This technology facilitates asynchronous communication between the two systems, guaranteeing accurate and efficient transfer of delivery documents from SAP ERP to SAP EWM. The amalgamation of ALE/IDoc, DRF, CIF, and qRFC techniques establishes a robust and dependable approach for integrating SAP ERP and SAP EWM in a decentralized EWM implementation on the SAP S/4HANA system.
Conclusion
The efficient data transfer strategies between SAP ERP or SAP S/4HANA and SAP EWM are vital for maintaining accurate and up-to-date information in the SAP Extended Warehouse Management (EWM) system. The master data replication process, particularly from SAP ERP or SAP S/4HANA to SAP EWM, plays a critical role in ensuring consistency and reflecting any changes made in the source systems. Different deployment scenarios, such as SAP NetWeaver, embedded EWM, and decentralized EWM, require unique considerations. For SAP NetWeaver deployments, CIF technology is instrumental in transferring master data, while qRFC technology facilitates the integration of transactional data. In embedded EWM, qRFC technology is crucial for transactional data, while master data transfer through CIF is unnecessary. Decentralized EWM implementations with SAP S/4HANA involve diverse techniques, including ALE/IDoc, DRF, CIF, and qRFC, for comprehensive data transfer.
The overall amalgamation of these techniques provides a robust and reliable means of integrating SAP ERP and SAP EWM in a decentralized EWM implementation on the SAP S/4HANA system. These strategies ensure harmonized and efficient operations, reflecting the commitment to data accuracy and real-time visibility in warehouse management processes.
Here’s where VE3 can help, we offer tailored solutions to streamline and optimize data transfer between SAP ERP or SAP S/4HANA and SAP EWM. Leveraging advanced integration capabilities and our partnership with SAP, we ensure seamless communication across systems, enhancing overall efficiency and accuracy in warehouse management. With a focus on delivering innovative solutions, we align with the complex requirements of SAP EWM implementations, contributing to a cohesive and reliable data transfer ecosystem. To know more, explore our innovative digital solutions or contact us directly.